Paternal leadership and its role in reducing workplace bullying: The mediating role of psychological well-being: Analytical research of the opinions of a sample of teachers working in schools in Babylon Governorate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71207/ijas.v20i82.2758Keywords:
paternalistic leadership, workplace bullying, psychological well-being.Abstract
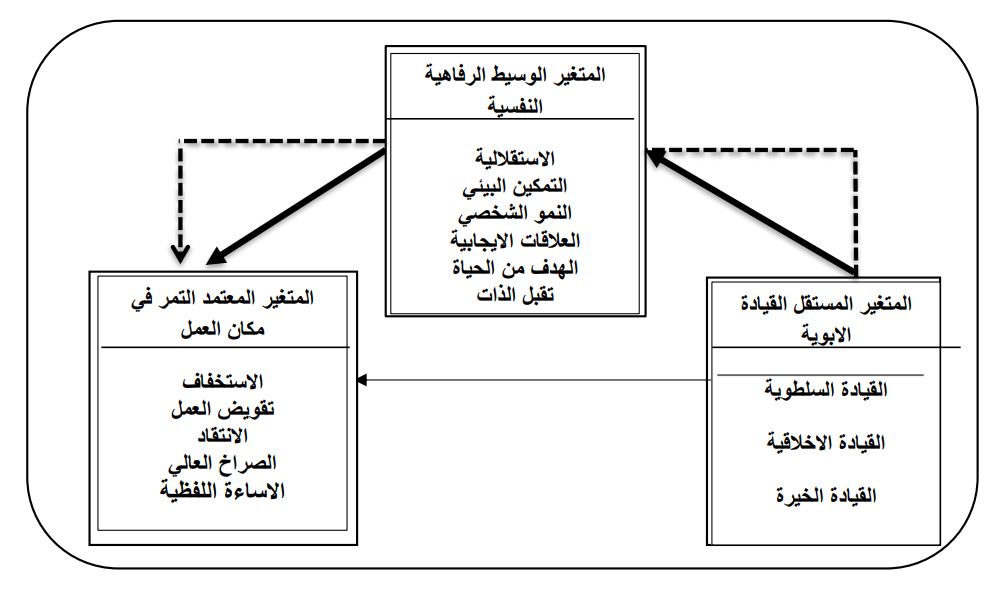
The research aimed to demonstrate the impact that paternal leadership exerts in reducing bullying in the workplace through the mediating role of psychological well-being at the level of a sample of teachers working in some schools in Babil Governorate. The problem was represented by several questions, the most important of which was (Does paternal leadership contribute to reducing or reducing bullying in the workplace in the studied schools. The descriptive analytical method was used as one of the methods used in social and administrative research. The questionnaire was used as a main tool in collecting data. The researched community consisted of four schools located in Babylon Governorate. The selected sample amounted to (100) teachers working in those schools. A number of statistical methods were used, including: normal distribution test, confirmatory factor analysis, and the following statistical programs were adopted (SPSS; Amos; Microsoft Excel). One of the most prominent results reached was that paternal leadership contributes to reducing bullying in the workplace, in addition to the psychological well-being variable mediating the relationship between the dependent and independent variables.
References
خلف، ياسر لطيف وعبد ، عذراء محسن ومحمود ، زيد خوام ، (2020) " القيادة الأبوية ودورها في الانغماس الوظيفي " ، مجلة كلية المعارف الجامعة ، المجلد 31 ، العدد 2 ،334-365 .
غالي ، حيدر حسين ، (2020) " تأثير القيادة الأخلاقية كمتغير تفاعلي في العلاقة بين سلوك العمل المنحرف والأزمات التنظيمية الداخلية " رسالة ماجستير ، كلية الإدارة والاقتصاد ، جامعة الكوفة .
محمد، وسام عبد الأمير،(2023)"الرفاهية النفسية وتأثيرها في الحد من سلوك التنمر في مكان العمل دراسة استطلاعية لعينة من الجامعات والكليات الاهلية في محافظة كربلاء المقدسة" رسالة ماجستير ، كلية الإدارة والاقتصاد ، جامعة كربلاء .
واعر، وسيلة ،(2020)" تأثير القيادة الابوية على أداء الموارد البشرية " مجلة الاستراتيجية والتنمية ، المجلد 10 ، العدد 4 ،30-49.
Arjanto, P., Bafadal, I., Atmoko, A., & Sunandar, A. (2023). https://ejce. cherkasgu. press. European Journal of Contemporary Education, 12(4).
Aybar, S., & Cark, O. (2023). Paternalistic leadership and work engagement in the innovative service industry: the mediating role of psychological contract. Marketing i menedžment innovacij, 14(4), 32-47.
Brotheridge, C. M., & Lee, R. T. (2007). Examining the relationship between the perceived work environment and workplace bullying. Canadian Journal of Community Mental Health, 25(2), 31-44.
Çevik, M. N., & Çevik, M. S. (2023). The Relationship between School Administrators' Paternalistic Leadership Behaviours and Teachers' Work Alienation Levels. European Journal of Educational Management, 6(1), 15-30.
Cheng, B. S., Chou, L. F., Wu, T. Y., Huang, M. P., & Farh, J. L. (2004). Paternalistic leadership and subordinate responses: Establishing a leadership model in Chinese organizations. Asian journal of social psychology, 7(1), 89-117.
Cheng, M. Y., & Wang, L. (2015). The mediating effect of ethical climate on the relationship between paternalistic leadership and team identification: A team-level analysis in the Chinese context. Journal of business ethics, 129(3), 639-654.
Cicellin, M., Mussolino, D., & Viganò, R. (2015). Gender diversity and father–daughter relationships: understanding the role of paternalistic leadership in family firm succession. International Journal of Business Governance and Ethics, 10(1), 97-118.
Dedahanov, A. T., Bozorov, F., & Sung, S. (2019). Paternalistic leadership and innovative behavior: Psychological empowerment as a mediator. Sustainability, 11(6), 1770.
Device, Gamian-Wilk, M .(2016). Personality traits as predictors or outcomes of being exposed to bullying in the workplace. Personality and Individual Differences, 115, 43.
Devonish, D. (2013). Workplace bullying, employee performance and behaviors: The mediating role of psychological well-being. Employee relations, 35(6), 630-647.
Dhanabhakyam, M., & Sarath, M. (2023). Psychological wellbeing: A systematic literature review. International journal of advanced research in science, communication and technology, 3(1), 603-607.
Di Martino, V. (2002). Workplace violence in the health sector. Country case studies Brazil, Bulgaria, Lebanon, Portugal, South Africa, Thailand and an additional Australian study. Ginebra: Organización Internacional del Trabajo, 3-42.
Edwards, M., & Blackwood, K. M. (2017). Artful interventions for workplace bullying: exploring forum theatre. Journal of Workplace Learning, 29(1), 37-48.
Edwards, S. D., Ngcobo, H. S., Edwards, D. J., & Palavar, K. (2005). Exploring the relationship between physical activity, psychological well-being and physical self-perception in different exercise groups. South African Journal for Research in Sport, Physical Education and Recreation, 27(1), 59-74.
Ghayas, M. M., Khan, M. M. S., Singh, E. P., Alajlani, S. E., & Ghafar, A. (2023). PATERNALISTIC LEADERSHIP AND ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT: EVIDENCE FROM THE INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SECTOR.
Ghosh, K. (2015). Benevolent leadership in not-for-profit organizations: Welfare orientation measures, ethical climate and organizational citizenship behaviour. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 36(5), 592-611.
Green, C., & Dimino Luong, A. (2023). Bullied: exploring the concepts of territorialism and groupthink involvement in workplace bullying. Nursing open, 10(10), 6777-6781.
Hanhimäki, E. (2023). Moral Professionalism in the Context of Educational Leadership. In Leadership in Educational Contexts in Finland: Theoretical and Empirical Perspectives (pp. 201-216). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
João, A. L., & Portelada, A. (2023). Coping with workplace bullying: Strategies employed by nurses in the healthcare setting. In Nursing Forum (Vol. 2023, No. 1, p. 8447804). Hindawi.
Khuwaja, U., Ahmed, K., Abid, G., & Adeel, A. (2020). Leadership and employee attitudes: The mediating role of perception of organizational politics. Cogent Business & Management, 7(1), 1720066.
Kim, J. A. (2023). Bullying Experiences of Workers in Small-Sized Workplaces: A Phenomenological Study. Sustainability, 15(21), 15436.
LaVan, H., & Martin, W. M. (2008). Bullying in the US workplace: Normative and process-oriented ethical approaches. Journal of business ethics, 83, 147-165.
Malik, A. J., & Santoso, C. B. (2022). The influence of paternalistic leadership on individual performance. Journal of Leadership in Organizations, 4(1).
Malik, N. A., & Björkqvist, K. (2019). Workplace bullying and occupational stress among university teachers: Mediating and moderating factors. Europe's journal of psychology, 15(2), 240.
Mazahreh, A., Hammad, H., & Abu-Jaber, H. (2009). The attitudes of instructors and faculty members about the quality of technical education programs in community colleges in Jordan. Journal of Social Sciences, 5(4), 401-407.
Pompeii, L., Dement, J., Schoenfisch, A., Lavery, A., Souder, M., Smith, C., & Lipscomb, H. (2013). Perpetrator, worker and workplace characteristics associated with patient and visitor perpetrated violence (Type II) on hospital workers: A review of the literature and existing occupational injury data. Journal of Safety Research, 44, 57-64.
Ryff, C. D. (2013). Psychological well-being revisited: Advances in the science and practice of eudaimonia. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 83(1), 10-28.
Savitri, M. D. (2024). Keseimbangan Kerja-Kehidupan Berpengaruh Pada Kesejahteraan Psikologis Pekerja. BULLET: Jurnal Multidisiplin Ilmu, 3(3), 420-431.
Strutyńska-Laskus, E., Madeja-Bień, K., & Gamian-Wilk, M. (2023). How the Workplace Influences Teachers’ Creativity: A Two-Wave Study on Workplace Bullying, Organisational Bullying Risk Factors and Creativity. Przegląd Badań Edukacyjnych (Educational Studies Review), 1(41), 139-162.
Ünler, E., & Kılıç, B. (2019). Paternalistic leadership and employee organizational attitudes: the role of positive/negative affectivity. Sage Open, 9(3), 2158244019862665.
Zanabazar, A., Jigjiddorj, S., & Jambal, T. (2023). Impact of Workplace Bullying on Job Burnout. Jurnal Ilmiah Peuradeun, 11(3), 1071-1090.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 College of Administration and Economics - University of Kerbala

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their papers without restrictions.









