The role of tacit knowledge in building core capabilities - an analytical study of the opinions of a sample of employees of the General Company for Mechanical Industries in Alexandria
an analytical study of the opinions of a sample of employees of the General Company for Mechanical Industries in Alexandria
Keywords:
Tacit knowledge, core capabilitiesAbstract
To distinguish any organization from other competitors is through a unique set of skills, these skills are called core competencies. With today's competition, knowledge is power, in front of other competing organizations. Intellectual capital management can be to be constrained, both large and small organizations have acquired information, and knowledge from organizations can be attributed to improvements
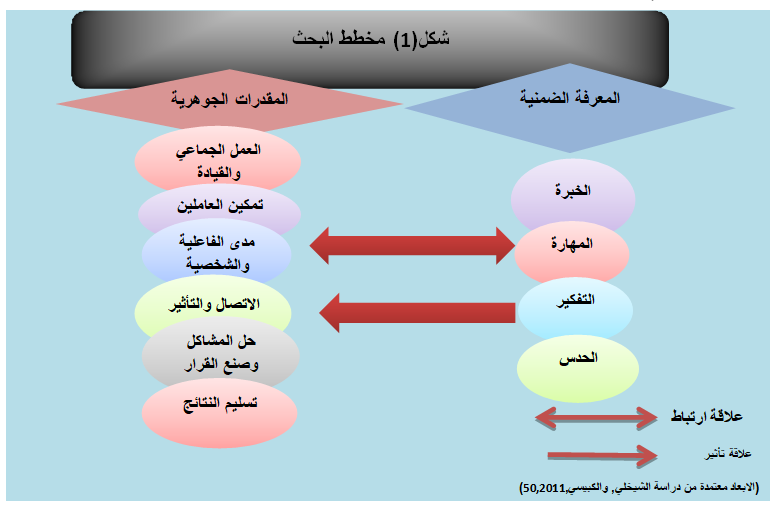
This research aim to identify the relationship between tacit knowledge and competencies in The General Company for Mechanical Industries in Alexandria. And for the reason of limited studies that dealt with the relationship between the two variables, especially in the Iraqi environment, the current research sought to address the two variables in order to study and determine the nature of the relationship between them, as well as the theoretical coverage of each. In order to achieve the objective of this research, two main hypotheses were tested; a random sample consisting of 72 employees of the surveyed company. The data were statistically processed using several statistical methods (simple correlation coefficient, simple regression analysis, T test, F test, interpretation coefficient). The research reached several conclusions, most notably as follow:
- The results of the statistical analysis confirm the acceptance of the first main research hypothesis (the existence of a positive relationship between the tacit knowledge and the competencies. This means that the respondents are aware of the importance of tacit knowledge which contributes to making the intrinsic capabilities more positive to achieve the organizational goals and improve the overall performance, in the sense that improving and increasing efficiency requires a lot of joint work.
- The company needs other core capabilities, such as the technology capabilities that are the basis of the company and complementary to other capabilities possessed by employees.
The research concluded with a number of recommendations, the most important of which is; “The need for management attention in the company in question, for the knowledge of the implicit knowledge to realize the intrinsic capabilities by increasing sales, building a brand, maintaining the competitive and financial position and the company".
References
اولاً : المصادر العربية :
- الشيخلي مهند محمد ياسين , الكبيسي صلاح الدين عواد كريم ,(2011) , دور المعرفة الضمنية في بناء المقدرات الجوهرية دراسة استطلاعية لا راء عينة من مديري ديوان الرقابة المالية في العراق, بحث منشور في مجلة جامعة الانبار للعلوم الاقتصادية والادارية 2011 المجلد الثالث , الاصدار السادس .
ثانياً : المصادر الانجليزي :
Arikan, C. L., & Enginoğlu, D. (2016). How elements of corporate culture affect overall firm performance. International Journal of Business Management and Economic Research (IJBMER), 7(3(.
Ayub, Y. I., Kogeda, O. P., & Lall, M. (2018). Capturing tacit knowledge: A case of traditional doctors in Mozambique. South African Journal of Information Management, 20(1).
Beets-Tan, R. G. H., Leijtens, J., Ziekenhuis, L., & Beets, G. L. (2011). Wait-and-see policy for clinical complete responders after chemoradiation for rectal cancer.
Bengtsson, E., & Andreasson, A. (2017). X. int: An internationalization service developed in collaboration with Cactus Utilities AB.
Brown, S., & Fai, F. (2006). Strategic resonance between technological and organisational capabilities in the innovation process within firms. technovation, 26(1).
Del Canale, M. (2013). Tacit Knowledge: How Do We Interpret It? A Qualitative Study of Knowledge Management in Knowledge-Intensive Firms.
Fouad, N. A., Grus, C. L., Hatcher, R. L., Kaslow, N. J., Hutchings, P. S., Madson, M. B., ... & Crossman, R. E. (2009). Competency benchmarks: A model for understanding and measuring competence in professional psychology across training levels. Training and Education in Professional Psychology, 3.
Hastjarjo, K., Yahya, D. K., Afiff, F., & Rufaidah, P. (2016). Core Competence on Real Estate Industry in Globalization Phenomenon: A Contemporary Approach. International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 6(6S).
Jones, K., & Leonard, L. N. (2009). From tacit knowledge to organizational knowledge for successful KM. In Knowledge Management and Organizational Learning (pp. 27-39). Springer, Boston, MA.
Mahroeian, H., & Forozia, A. (2012). Challenges in managing tacit knowledge: A study on difficulties in diffusion of tacit knowledge in organizations. International Journal of Business and Social Science, 3(19).
Mazzarol,Tim&Soutar,JeafferyNorman,(1999),”Sustainable Advantage for Educational in Situations, The International Journal of Educational Management,13/6.
Mládková, L. (2011). Sharing tacit knowledge within organizations: Evidence from the Czech Republic.
Mohajan, H. (2017). Tacit Knowledge for the Development of Organizations.
Pathirage, C. P., Amaratunga, D., & Haigh, R. (2008). The role of tacit knowledge in the construction industry: towards a definition.
Traynor, E.(2014) Do Barriers Exist to the Transfer of Tacit Knowledge?.
UYSAL, G. (2007). Core Competence: A Competitive Base for Organizational Success.
Vignoles, V. L., Schwartz, S. J., & Luyckx, K. (2017). Introduction: Toward an integrative view of identity. In Handbook of identity theory and research (pp. 1-27). Springer, New York, NY.
Virtanen, I. (2010). Epistemological problems concerning explication of tacit knowledge. Journal of Knowledge Management Practice, 11(4).
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Economics and Administration College - Karbala University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their papers without restrictions.



